The Tata Group, one of the most respected and diversified conglomerates globally, has a rich history that spans over 150 years. Established by Jamsetji Tata in 1868, the Tata Group has grown from a small trading firm to a global enterprise, with operations in more than 100 countries and a workforce exceeding 750,000 employees. The Tata Group’s journey is a testament to its commitment to innovation, integrity, and excellence.
The Foundation of the Tata Group
The Tata Group’s story began in 1868 when Jamsetji Tata, often regarded as the “Father of Indian Industry,” founded a trading company in Bombay (now Mumbai). His vision was to build a strong industrial base in India that could compete on a global scale. Jamsetji Tata’s pioneering spirit led to the establishment of several key industries in India, including steel, power, and hospitality.
One of his most significant contributions was the establishment of Tata Steel, India’s first steel plant, in 1907. This marked the beginning of India’s industrialization and laid the foundation for the Tata Group’s future growth. Tata Steel, headquartered in Jamshedpur, remains one of the world’s leading steel producers today.
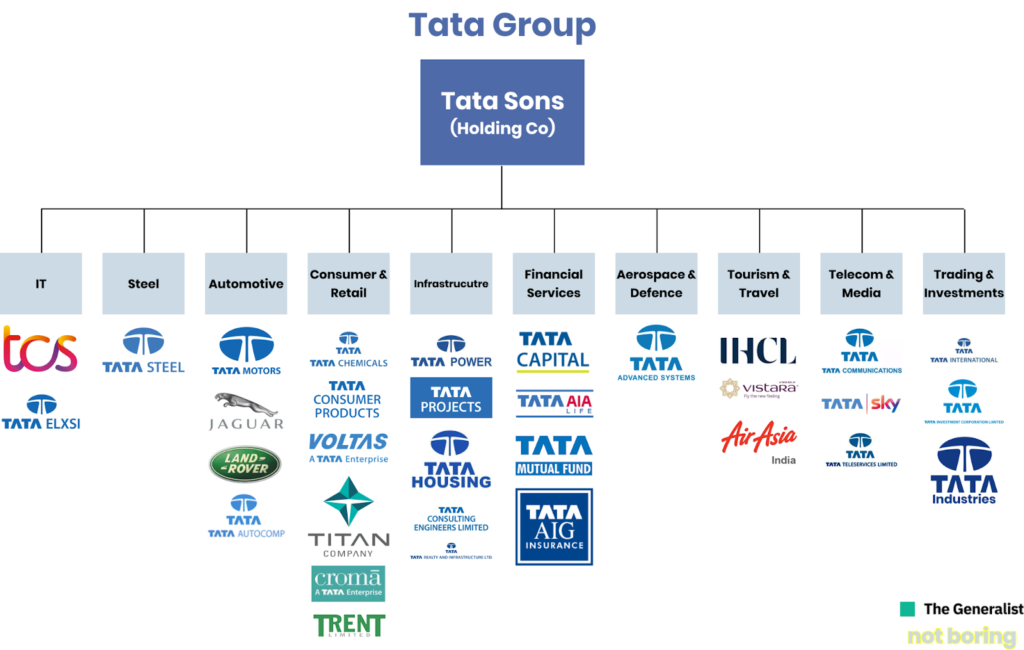
Expansion and Diversification
After Jamsetji Tata’s passing, his successors, including his sons Dorabji Tata and Ratanji Tata, continued to expand the group’s operations. The Tata Group diversified into various sectors, including chemicals, automobiles, consumer goods, and information technology. This diversification was driven by a commitment to contribute to the nation’s development and improve the quality of life for its people.
The Tata Group’s foray into the automobile industry began with the establishment of Tata Motors in 1945. Tata Motors quickly became a key player in the Indian automotive market, producing a range of vehicles, from commercial trucks to passenger cars. The launch of the Tata Indica in 1998 marked a significant milestone, as it was the first car designed and manufactured entirely in India.
Global Expansion and Acquisitions
In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, the Tata Group began to expand its footprint globally. Under the leadership of Ratan Tata, the group pursued several high-profile acquisitions, including the purchase of Tetley Tea (UK) in 2000, Daewoo Commercial Vehicles (South Korea) in 2004, and the iconic British brands Jaguar Land Rover in 2008. These acquisitions not only expanded the Tata Group’s global presence but also enhanced its capabilities in various industries.
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS), the group’s flagship IT services company, has been a major driver of the Tata Group’s global growth. Established in 1968, TCS is now one of the world’s largest IT services companies, providing technology solutions to clients across various industries. TCS’s success has been instrumental in positioning the Tata Group as a global leader in the technology sector.
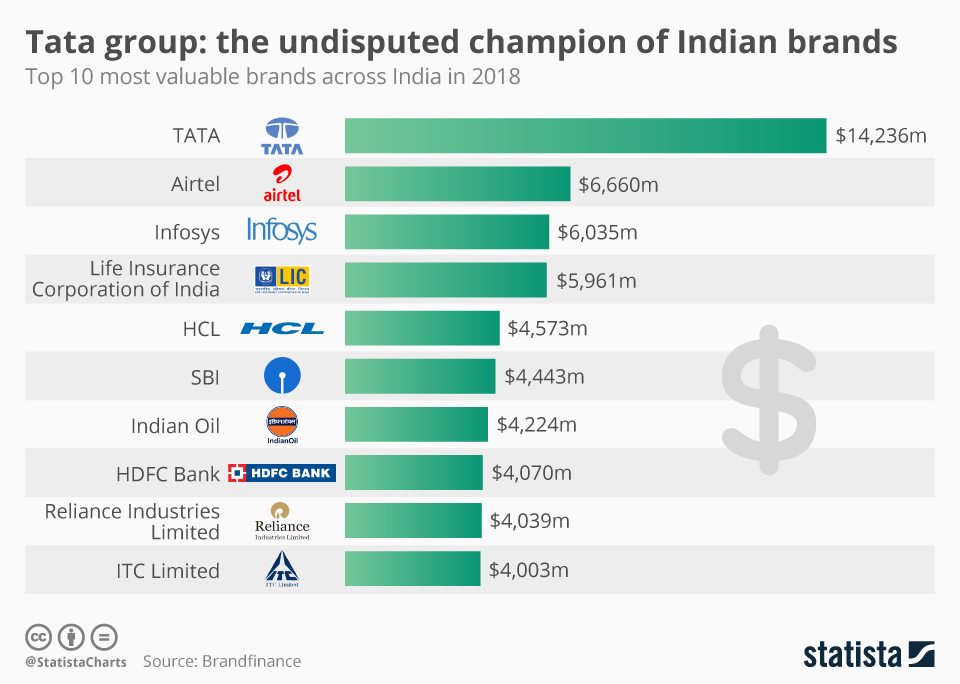
Commitment to Sustainability and Social Responsibility
The Tata Group has always been guided by a strong sense of social responsibility. The group’s commitment to ethical business practices and corporate social responsibility (CSR) is deeply ingrained in its corporate philosophy. The Tata Trusts, which own a significant portion of Tata Sons, the holding company of the Tata Group, have been instrumental in funding numerous philanthropic initiatives in areas such as education, healthcare, and rural development.
The Tata Group is also committed to sustainability and environmental stewardship. Tata Power, one of India’s largest integrated power companies, has been at the forefront of promoting renewable energy in the country. The group’s focus on sustainability is evident in its efforts to reduce its carbon footprint and promote green technologies across its businesses.
Innovation and the Future
Innovation has always been a cornerstone of the Tata Group’s success. The group has consistently invested in research and development (R&D) to drive innovation across its various businesses. Tata Motors, for example, has been a pioneer in electric vehicle (EV) technology in India, with the launch of the Tata Nexon EV, one of the best-selling electric cars in the country.
The Tata Group’s commitment to innovation extends beyond its traditional businesses. Tata Digital, the group’s digital arm, is focused on leveraging technology to create new business models and drive growth in the digital economy. Tata Neu, the group’s super app, is an example of its efforts to integrate its various services and provide a seamless digital experience to customers.
Conclusion
The Tata Group’s journey from a small trading firm to a global conglomerate is a remarkable story of vision, resilience, and excellence. The group’s commitment to innovation, sustainability, and social responsibility has made it a trusted name in India and around the world. As the Tata Group continues to grow and evolve, it remains true to the values and principles laid down by its founder, Jamsetji Tata, over 150 years ago.













